# Component Troubleshooting Components may fail for different reasons. In this guide, we will show you how to troubleshoot in the kubernetes cluster. ## Table of contents - [Accessing the kubernetes cluster](#accessing-the-kubernetes-cluster) - [Kubeconfig](#kubeconfig) - [Logs](#logs) - [Exec](#exec) - [Run](#run) - [Copy](#copy) ## Accessing the kubernetes cluster The kubernetes cluster includes a rancher server that allows you to access the kubernetes cluster. The rancher server is available at https://k8so.emerald.digital.tecnalia.dev/.   There you can access the kubernetes cluster and check the deployment of the component. 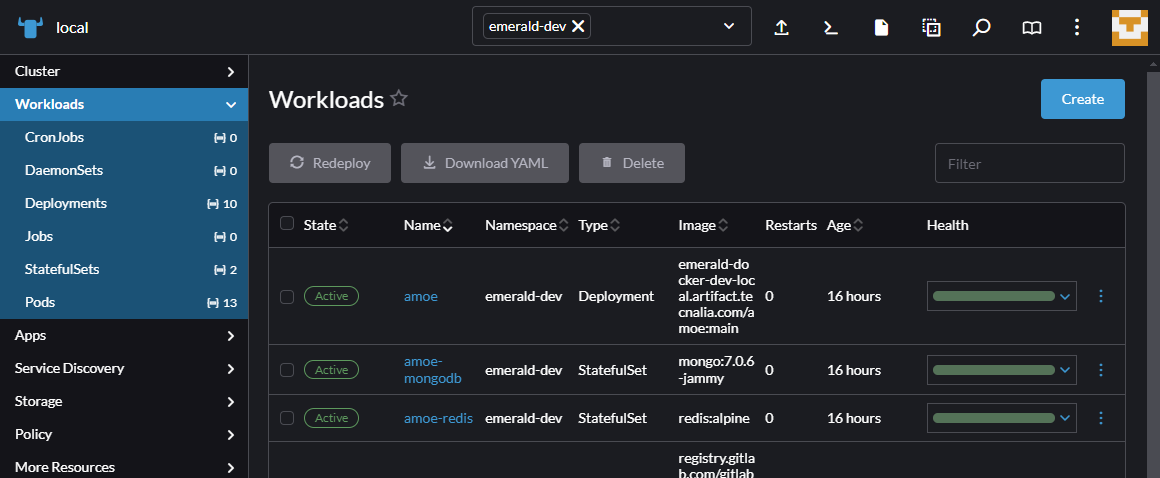 ## Kubeconfig For troubleshooting in a terminal with kubectl, you need to download the kubeconfig file. To get the kubeconfig login into kubernetes https://k8so.emerald.digital.tecnalia.dev/ and download the kubeconfig. **Be aware that the kubeconfig is valid for one month**. 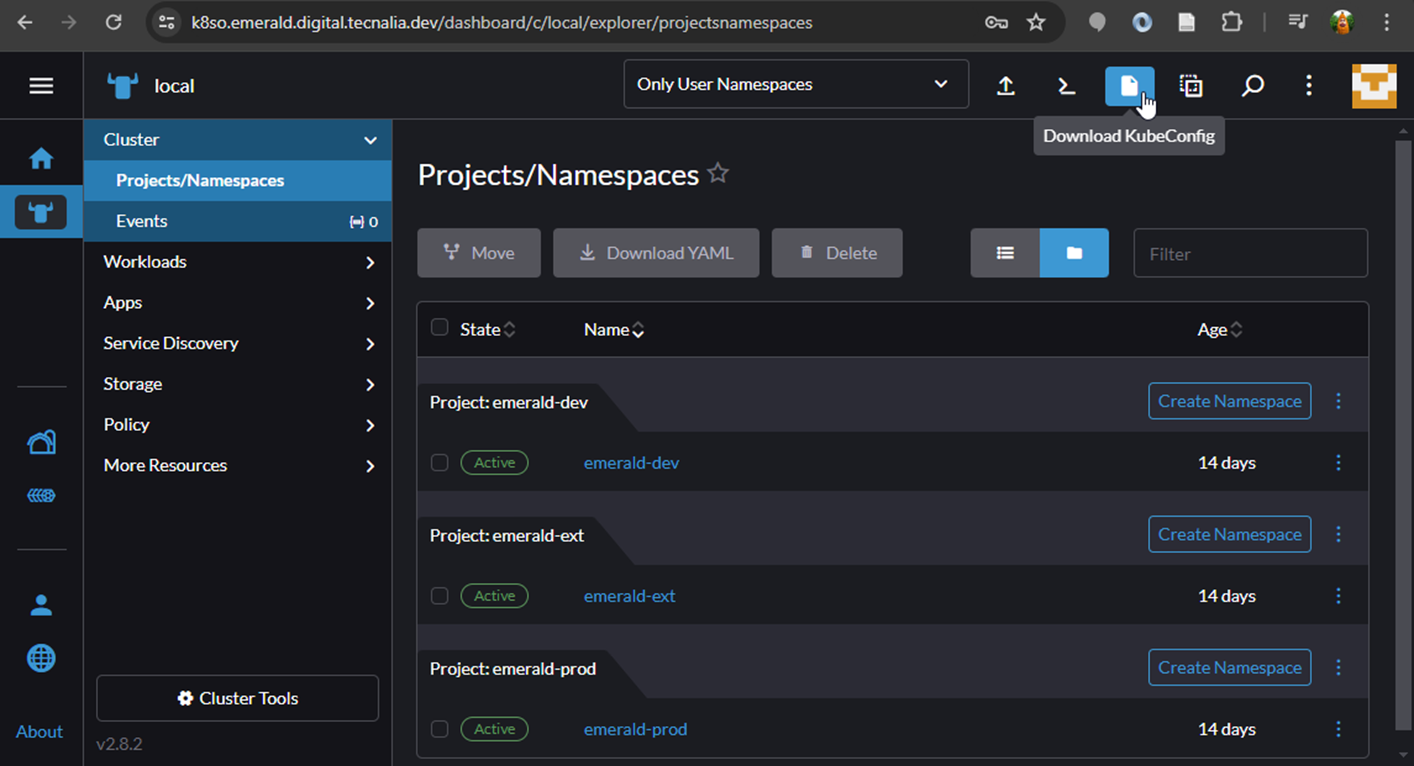 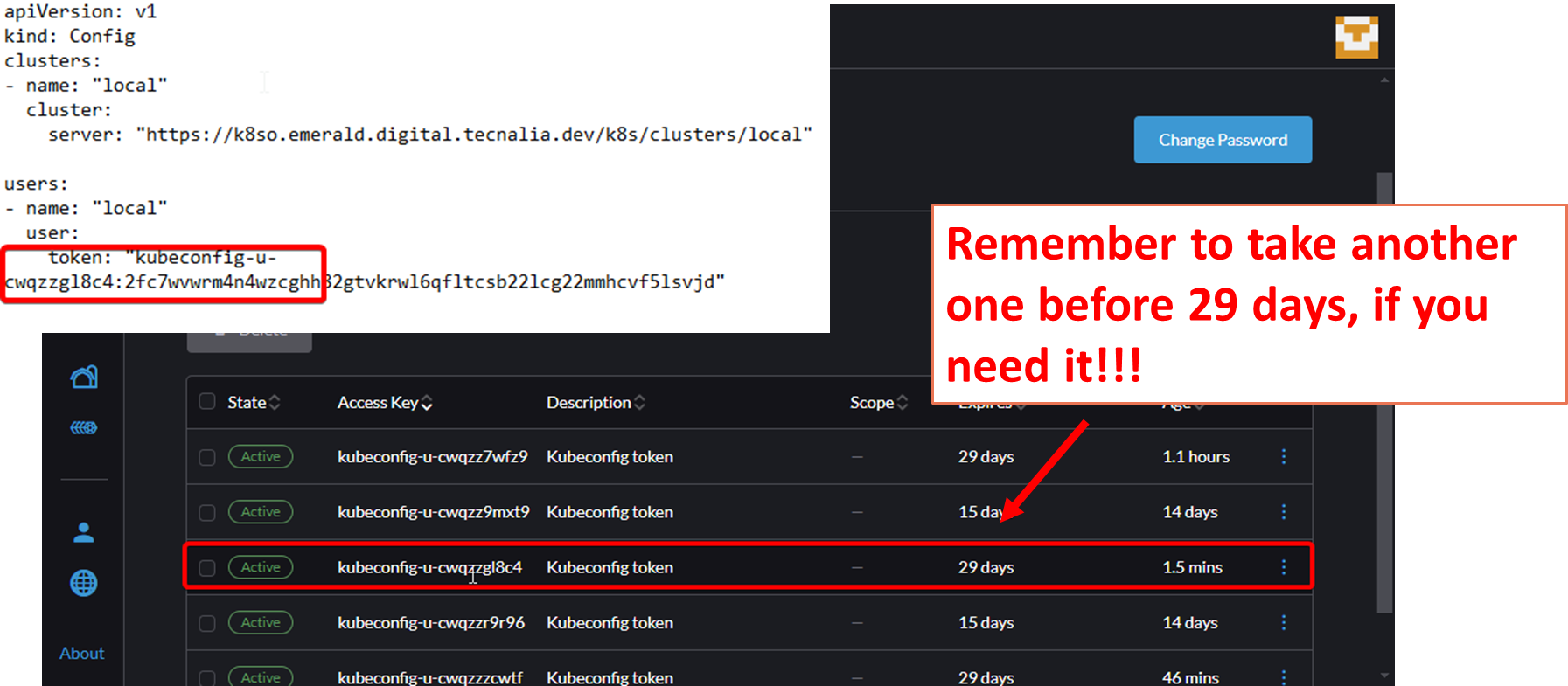 The kubeconfig should be stored in the `~/.kube/config` file. ```bash cat << EOF > ~/.kube/config <content of the kubeconfig file> EOF ``` 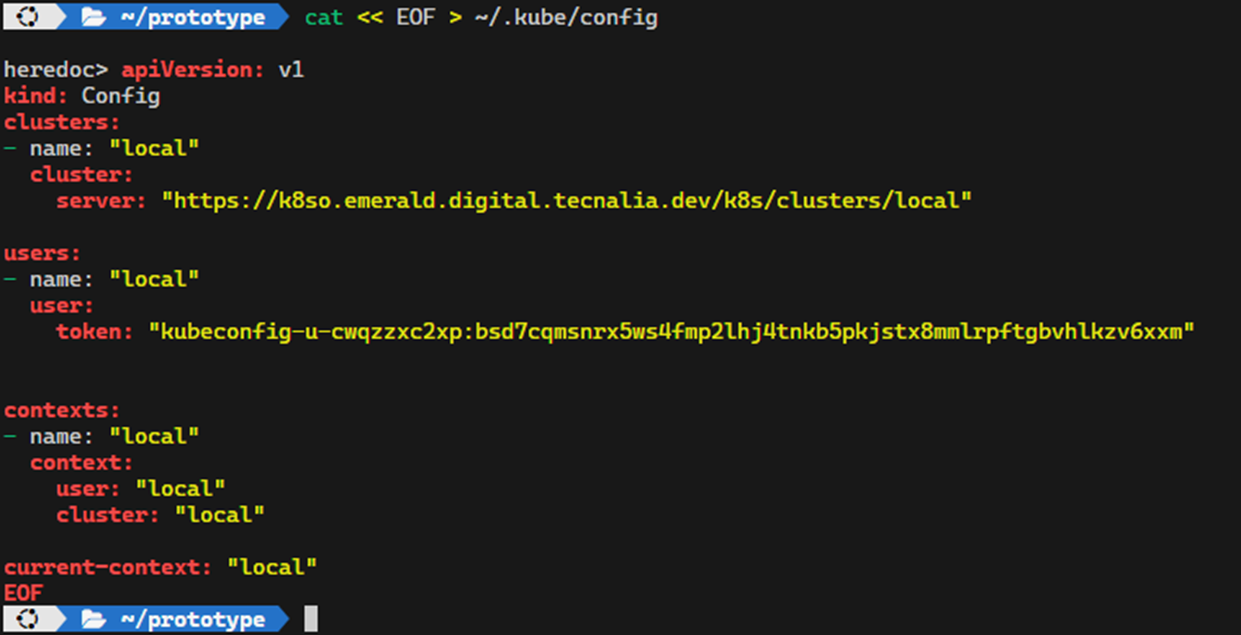 ```bash kubectl config get-contexts kubectl config use-context local ``` The above is valid for one kubernetes cluster. If you have more than one kubernetes cluster, you can store the kubeconfig in different files and use the `KUBECONFIG` environment variable to select the kubeconfig file. ## Logs Logs of a pod of a can be accessed using the rancher UI or the kubectl command. ```bash kubectl -n emerald-dev logs –f <pod-name> ``` We can also access using the deployment name. ```bash kubectl -n emerald-dev logs –f deployment/<deployment-name> -c <container-name> ``` ## Exec To check what has inside a container, install packages, curl, nslookup, … ```bash kubectl -n emerald-ext exec -it <pod-name> -- /bin/bash ``` `/bin/bash` is the shell that will be executed in the container. If the container does not have `/bin/bash`, you can try to use `/bin/sh`. This will depend on the base image of the container. ## Run Sometimes we need to run a container in the same internal network to check services, pods, ports, etc. ```bash kubectl -n emerald-ext run -i --tty --rm --image busybox --restart=Never -- /bin/bash ``` Replace `busybox` with the image you want to run. Remember that the `/bin/bash` is the shell that will be executed in the container. If the container does not have `/bin/bash`, you can try to use `/bin/sh`. This will depend on the base image of the container. ## Copy To copy files from a container to the local machine, we can use the `kubectl cp` command. This can be handy for backup purposes. ```bash kubectl -n emerald-ext cp <pod-name>:<path-in-container> <path-in-local-machine> ``` For example, to copy the file `/etc/hosts` from the pod `my-pod` to the local machine, we can use the following command: ```bash kubectl -n emerald-ext cp my-pod:/etc/hosts /tmp/hosts ``` You can also copy files from the local machine to the container. ```bash kubectl -n emerald-ext cp /tmp/hosts my-pod:/etc/hosts ```